
Colon Polyps – A Complete Overview
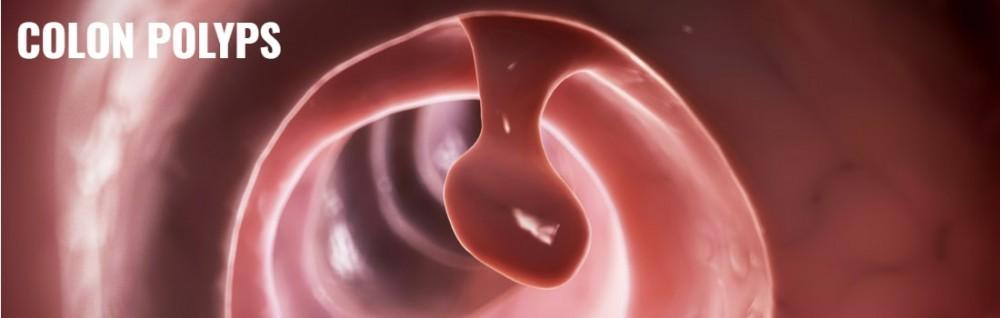
Polyps are an extra piece of tissue that cultivates inside the body. What are colon polyps? Colon polyps develop in the large intestine or colon. Most of these are not life-threatening. Nevertheless, polyps may turn into cancer or at present be cancer already. In order to be safe, doctors eliminate polyps and check them for the presence of cancer cells.
Read below about the colon polyps’ symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention:

WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF COLON POLYPS?
Colon Polyps are not detectable since they typically don’t root indicators. These growths are generally found through repetitive screening examinations for colon cancer. The test looks for signs of a sickness when there are no symptoms. The symptoms of colon polyps appear when the polyps get big. You can have bleeding from your rectum or an alteration in your bowel habits. A change in bowel habits comprises diarrhea, constipation, going to the bathroom more often or less often than usual, or a change in the way your stool looks.
When to see a doctor:
If you feel these symptoms visit your doctor right away:
- Stomach pain
- Blood in stool
- An alteration in your bowel behaviors that lasts extensive than a week

WHAT CAUSES COLON POLYPS?
Colon polyps’ causes are unclear, nonetheless, there are risk factors for developing one.
Polyps in the colon are separated into three types:
- Hyperplasticcolon polyps – These are non-threatening lumps, and encompasses about 90% of it.
- Adenomas – They are colon polyps that are typically small, have a small probability of malignancy, and involve about 10% of polyps. The 3 three types of adenomas are a tubular adenoma, tubulovillous adenoma, and villous adenoma.
- Polyposis syndromes – A cluster of hereditary disorders that yield among other things, colon polyps)
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPING COLON POLYPS?
These are the known risk factors for the condition:
- Familial history of colon polyps
- Familial history of colon cancer
- High intake of red meats
- Nourishment high in processed meats
- History of inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
- Inherited conditions
- Older age
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF COLON POLYPS?
Selected colon polyps may convert to be cancerous. The earlier polyps are detached, the less likely it is that they will develop malignantly.

HOW TO DIAGNOSE COLON POLYPS?
A gastroenterologist usually diagnoses colon polyps after collation and execution of several diagnostic exams which may include:
- Stool tasters confirmed for blood
- Rectal exam
- Barium enema
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Capsule endoscopy by the camera
- Virtual colonoscopy
- Discovery of mutant, fragmented and/or methylated DNA in the stool
- A biopsy can define benign vs. malignant pre-cancerous or cancerous polyps

WHAT IS THE TREATMENT OF COLON POLYPS?
Medical colon polyps’ treatment or management with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) has revealed in some educations to cut the size and number of colon polyps. But, there is no signal that they can avert cancer development. One study recommends aspirin may moderate persistent colon polyps.
Patients known to have a small volume of polyp growth are the one can undergo polypectomy, a technique that permits removal of the polyps through colonoscopy. Sometimes Colonic resection is used if multiple intestinal polyps are connected with syndromes like familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). This kind of procedure should be discussed between the patient and his/her gastroenterologist.
HOW TO PREVENT COLON POLYPS?
A person can prominently reduce the risk of colon polyps and colorectal cancer by taking regular screenings. These lifestyle variations also can support:
Consume plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains in your nutrition and lessen your fat consumption. Take a limit on alcohol consumption and quit tobacco smoking. Stay substantially active and uphold a healthy body weight.
Ask your physician about calcium and vitamin D. Research found out that increasing your consumption of calcium aids to avoid the return of colon adenomas. Other studies have shown that vitamin D has shielding outcome to colorectal cancer.
Ponder your options if at risk. Check your family history of colon polyps, contemplate having genetic counseling. When you are identified with a hereditary disorder that affects colon polyps, regular colonoscopies are subject to be needed in young adulthood.

TO CONSULT A GASTROENTEROLOGIST, VISIT GI ENDOSCOPY PRACTICE IN NJ:
If you’re looking for an American board-certified gastroenterologist, you can visit GI Endoscopy Practice and consult Dr. Bharat Dasani who offers the best treatment for colon polyps while customizing it according to your condition and needs. For more information or to book an appointment, visit our website and fill up the online contact us form or call 973.248.1550 for an immediate response.
*** The material/advice presented in this article doesn’t constitute a professional medical advice. It is intended to help the patients looking for general information about colon polyps ***
You Might Also Enjoy...


What Is The Natural Treatment For H. Pylori Infection?
A Complete Overview of Hiatal Hernia

Constipation – How To Use The Best 5 Essential Oils?

How The Procedure Of Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Is Performed

